Device and sensors
In this example, the MKR1000 is equipped with sensors that measure temperature, humidity, CO2 and the total amount of volatile organic compounds (TVOCs). To measure temperature and humidity, we used the same sensor as in the section Temperature and humidity from Chapter 2, the AM2302. To measure CO2 and TVOCs, the SparkFun Air Quality Breakout CCS811 is used. It can do TVOC sensing from 0 to 1,187 parts per billion and CO2 sensing from 400 to 8,192 parts per million. The breakout board is shown below:
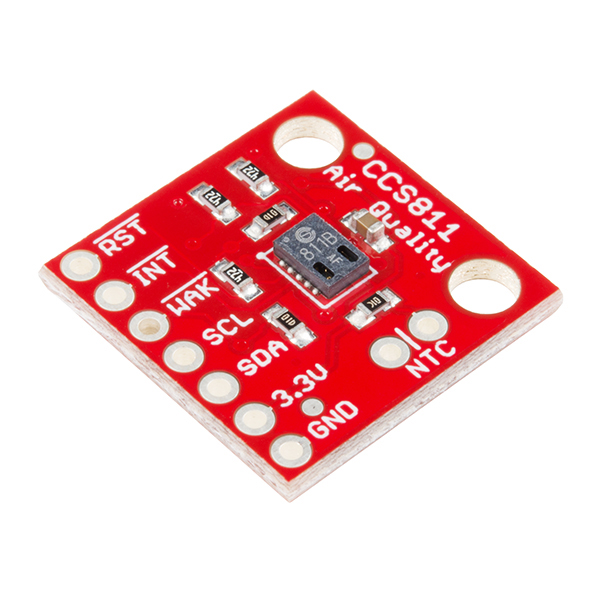
The board is connected to the MKR1000 using the I²C interface. SparkFun is known for great documentation which is apparent when you read the hookup guide. It contains all the details you need to connect the board and use the associated Arduino library.
When you start the device and look at the sensor readings, you will notice that co2 and tvoc start at 400 and 0 which are the default values. It is very common for sensors to have a warm up time, and this sensor is no different. You need to wait around 20 minutes before the sensor will deliver good values. And even then you can debate about the validity of the sensor readings. In this case, CO2 (actually eCO2 from "equivalent CO2") is derived from the total amount of volatile organic compounds. In some cases, the calculated eCO2 can be very different from the actual CO2 level depending on the composition of volatile organic compounds in the air. Nevertheless, this approach is used by many commercial devices. One such device is the Foobot for instance.
This book is about building IoT solutions so we will leave the air quality science to the scientists. Let's have a look at the device code:
#include <SparkFunCCS811.h>
#include <RTCZero.h>
#include <sha256.h>
#include <Base64.h>
#include <DHT.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <WiFi101.h>
#include <PubSubClient.h>
#include <ArduinoJson.h>
#define DHTPIN 2 // Pin which is connected to the DHT sensor.
#define DHTTYPE DHT22 // DHT 22 (AM2302)
#define CCS811_ADDR 0x5B //Default I2C Address (CCS811)
// init DHT with pin and type
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
// dynamic Json buffer for desired property notifications
DynamicJsonBuffer jsonDesiredProperties;
// ssid and password of WiFi network
char ssid[] = "WIFI_SSID";
char pass[] = "WIFI_PASSWORD";
// initial WiFi status
int status = WL_IDLE_STATUS;
// MQTT connectivity variables
const char mqtt_client[] = "DEVICEID";
const char mqtt_server[] = "IOTHUBNAME.azure-devices.net";
const int mqtt_port = 8883;
const char mqtt_user[] = "IOTHUBNAME.azure-devices.net/DEVICEID/api-version=2016-11-14";
// SAS token variables
char device_key[] = "DEVICEKEY";
String device_url = String(mqtt_server) + "/devices/" + String(mqtt_client);
long expire_time = 60 * 60 * 24; // 24 hours
// MQTT callback
void callback(char* topic, byte* payload, unsigned int length);
// use the generic SSL client in combination with PubSubClient
WiFiSSLClient wifiClient;
PubSubClient client(mqtt_server, mqtt_port, callback, wifiClient);
// vars for measuring every x seconds instead of delay
unsigned long previousMillis = 0;
long interval = 5000;
// RTC
RTCZero rtc;
const int GMT = 0;
// CCS811
CCS811 vocs(CCS811_ADDR);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for the serial port to not miss messages - so open the serial monitor!!!
}
Serial.print("Checking for WiFi: ");
if (WiFi.status() == WL_NO_SHIELD) {
Serial.println("NOT AVAILABLE!");
return;
}
Serial.println("PRESENT!");
// try to connect to WiFi network
while ( status != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.print("Connecting to: ");
Serial.println(ssid);
status = WiFi.begin(ssid, pass);
// wait 10 seconds for connection:
delay(10000);
}
// we are connected now
Serial.println("Connected to WiFi!");
printWiFiStatus();
// init rtc; taken from https://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/WiFiRTC
rtc.begin();
unsigned long epoch;
int numberOfTries = 0, maxTries = 6;
do {
epoch = WiFi.getTime();
numberOfTries++;
}
while ((epoch == 0) || (numberOfTries > maxTries));
if (numberOfTries > maxTries) {
Serial.print("NTP unreachable!!");
while (1);
}
else {
Serial.print("Epoch received: ");
Serial.println(epoch);
rtc.setEpoch(epoch);
Serial.println();
}
// vocs sensor init
CCS811Core::status returnCode = vocs.begin();
if (returnCode != CCS811Core::SENSOR_SUCCESS)
{
Serial.println("vocs.begin() returned with an error.");
while (1); // we don't continue
}
// temperature & humidity init
dht.begin();
}
void loop() {
// connect or reconnect to MQTT server
if (!client.connected()) {
reconnect(); // blocking
}
// get the current millis
unsigned long currentMillis = millis();
if(currentMillis - previousMillis >= interval) {
// reset the timer
previousMillis = currentMillis;
// get temperature and humidity from DHT22
float h = dht.readHumidity();
// Read temperature as Celsius
float t = dht.readTemperature();
// Check if any reads failed and exit early (to try again).
if (isnan(h) || isnan(t)) {
Serial.println("Failed to read from DHT sensor!");
return;
}
// get vocs and eco2
int co2, tvoc;
if (vocs.dataAvailable())
{
vocs.readAlgorithmResults();
//vocs.setEnvironmentalData(h, t);
co2 = vocs.getCO2();
tvoc = vocs.getTVOC();
}
// build Json string and convert to char array for client.publish
String postData = "{\"temperature\":" + String(t) + ",\"humidity\":" + String(h) + ",\"co2\":" + String(co2) + ",\"tvoc\":" + String(tvoc) +"}";
char postBuffer[postData.length()+1];
postData.toCharArray(postBuffer, postData.length()+1);
Serial.println(postBuffer);
// publish message to MQTT server
client.publish("devices/mkr1000/messages/events/", postBuffer);
}
client.loop();
}
void printWiFiStatus() {
// print the SSID of the network you're attached to:
Serial.print("SSID: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.SSID());
// print your WiFi shield's IP address:
IPAddress ip = WiFi.localIP();
Serial.print("IP Address: ");
Serial.println(ip);
// print the received signal strength:
long rssi = WiFi.RSSI();
Serial.print("signal strength (RSSI):");
Serial.print(rssi);
Serial.println(" dBm");
}
void reconnect() {
// Loop until we're reconnected
while (!client.connected()) {
Serial.print("Attempting MQTT connection...");
// generate SAS token on the fly
String mqtt_pass=generateSAS(device_url, device_key, expire_time);
char passBuffer[mqtt_pass.length()+1];
mqtt_pass.toCharArray(passBuffer, mqtt_pass.length()+1);
// Attempt to connect
if (client.connect(mqtt_client, mqtt_user, passBuffer)) {
Serial.println("connected");
// subscribe to D2C messages
client.subscribe("devices/mkr1000/messages/devicebound/#");
// subscribe to operation responses
client.subscribe("$iothub/twin/res/#");
// subscribe to desired property updates
client.subscribe("$iothub/twin/PATCH/properties/desired/#");
} else {
Serial.print("failed, rc=");
Serial.print(client.state());
Serial.println(" try again in 5 seconds");
// Wait 5 seconds before retrying (blocking)
delay(5000);
}
}
}
void callback(char* topic, byte* payload, unsigned int length) {
Serial.print("MQTT message arrived on topic: ");
Serial.println(topic);
// check if a messages comes in on $iothub/twin/PATCH/properties/desired/?$version={new version}
// it is a desired property update notification
if (String(topic).startsWith("$iothub/twin/PATCH/properties/desired")) {
parseDesiredProperties(payload);
}
}
void parseDesiredProperties(byte* payload) {
JsonObject& root = jsonDesiredProperties.parseObject(payload);
if(root.success()) {
Serial.println("Parsed desired properties");
int newMillis=root["reportInterval"];
if(newMillis > 2999 && newMillis < 120001) {
interval = newMillis;
String postProperty = "{\"reportInterval\":" + String(newMillis) + "}";
char postBuffer[postProperty.length()+1];
postProperty.toCharArray(postBuffer, postProperty.length()+1);
client.publish("$iothub/twin/PATCH/properties/reported/?$rid=1", postBuffer);
Serial.print("Set new interval to: ");
Serial.println(newMillis);
}
} else {
Serial.println("Could not parse desired properties");
}
}
//http://hardwarefun.com/tutorials/url-encoding-in-arduino
String urlEncode(const char* msg)
{
const char *hex = "0123456789abcdef";
String encodedMsg = "";
while (*msg!='\0'){
if( ('a' <= *msg && *msg <= 'z')
|| ('A' <= *msg && *msg <= 'Z')
|| ('0' <= *msg && *msg <= '9') ) {
encodedMsg += *msg;
} else {
encodedMsg += '%';
encodedMsg += hex[*msg >> 4];
encodedMsg += hex[*msg & 15];
}
msg++;
}
return encodedMsg;
}
// from https://github.com/andriyadi/AzureIoTHubMQTTClient
String generateSAS(String url, char* key, long expire) {
// if expire is 0 then default to January 1, 2030 for now
if( expire==0 ) {
expire = 1893456000;
} else {
expire = rtc.getEpoch() + expire;
}
// create the string to sign which is the url + newline + expire
//url is IOTHUBNAME.azure-devices.net/devices/DEVICEID
url.toLowerCase();
String stringToSign = url + "\n" + String(expire);
// the signing key is a device key and needs to be
// base64 decoded; decoded key in decodedKey variable
int keyLen = strlen(key);
int decodedLen = base64_dec_len(key, keyLen);
char decodedKey[decodedLen];
base64_decode(decodedKey, key, keyLen);
// create the signature with the Sha256 library
Sha256.initHmac( (const uint8_t*)decodedKey, decodedLen);
Sha256.print(stringToSign);
char* signature = (char*) Sha256.resultHmac();
// the signature is base64 encoded
int encodedLen = base64_enc_len(32);
char encodedSign[encodedLen];
base64_encode(encodedSign, signature, 32);
// create SAS and url encode the base64 encoded signature
return "SharedAccessSignature sr=" + url + "&sig=" + urlEncode(encodedSign) + "&se=" + String(expire);
}
void printTime()
{
print2digits(rtc.getHours() + GMT);
Serial.print(":");
print2digits(rtc.getMinutes());
Serial.print(":");
print2digits(rtc.getSeconds());
Serial.println();
}
void printDate()
{
Serial.print(rtc.getDay());
Serial.print("/");
Serial.print(rtc.getMonth());
Serial.print("/");
Serial.print(rtc.getYear());
Serial.print(" ");
}
void print2digits(int number) {
if (number < 10) {
Serial.print("0");
}
Serial.print(number);
}
You will notice that the SparkFunCCS811 library is used to work with the CCS811 breakout board. The default I²C address of the device is 0x5B as set by the #define CCS811_ADDR. Here is a quick recap of the other libraries:
- RTCZero: to interact with the real-time clock of the MKR1000; time is required to set the validity of the SAS token that is used to authenticate to IoT Hub
- sha256 and Base64: required to generate the SAS token as discussed in Connect with MQTT in Chapter 3
- DHT: to obtain temperature and humidity readings
- SPI and WiFi101: to interact with the WiFi chip of the MKR1000
- PubSubClient: generic MQTT library to connect to IoT Hub
Because we now generate the SAS token dynamically, the device's symmetric key is required in addition to a device url. We also need the amount of seconds that the token should be valid (set to 24 hours):
// SAS token variables
char device_key[] = "DEVICEKEY"; //symmetric key
String device_url = String(mqtt_server) + "/devices/" + String(mqtt_client);
long expire_time = 60 * 60 * 24; // 24 hours
As discussed in Connect with MQTT, you can set the report interval by modifying the reportInterval desired property of the device twin. Valid values are between 3000 and 120000 milliseconds.
We will now connect Stream Analytics to the IoT Hub that receives our sensor values and do meaningful things such as archiving the readings and forwarding the readings to a real-time Power BI dashboard.